Human Scene Simulation
This component is created to simulate an environment, where several people interact with each other based on the dataset.
The component can be found at the robocomp-viriato directory with the name “HumanSceneSim.”
Video Demo can be found at https://youtu.be/dUrtZGbO7Oc
Dataset Used
Here We are using the SALSA Dataset
-
The purpose of this component is to create a specific agent with a new graphical interface that allows, frame by frame, to update the position of a person, or a group of people, in the environment - and, therefore, in the DSR.
-
This dataset contains a frame by frame position change of the persons.
About the Dataset
-
The first column of all modalities is the timestamp in SECONDS from the first visual images
-
The Position/pose related to persons are stores in the geometryGT
-
These are the columns
Timestamp[s] , Ground_Position_X[m] , Ground_Position_Y[m] , Useless_Field , Body_Pose[rad] , Relative_Head2Body_Pose[rad] , Validity[bool] -
Each CSV file in the geometryGT folder corresponds to a person with the ID as the name of the CSV file.
-
there are two different scenes:
How we have proceeded
-
The first step is to get to know about the dataset, what each column signifies and how to use these value to recreate the environment, also filter out unnecessary columns.
-
Data Extraction from the CSV file is done using
extractCSVfunction, which uses File stream to fetch the data from the CSV. -
These data are then stored in a
PersonCsvDataClass. -
This class stores only a single frame of the person’s pose data.
-
A vector of PersonCsvData
vector<PersonCsvData> personCsvis used to store all the pose frame of a particular person. -
These Person specific pose data is now mapped with the ID of the Person, and stored as
map<int, vector<PersonCsvData>> PersonAvailable
UI Perspective
-
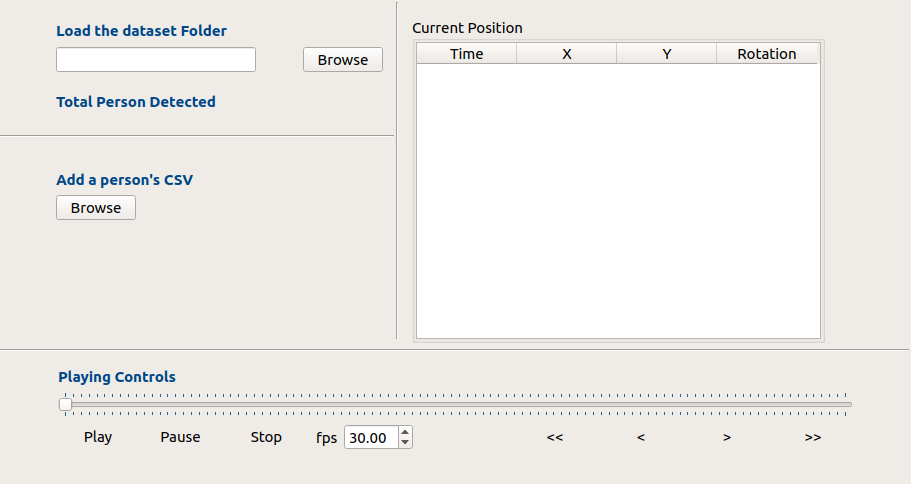
Two Separate options are given to the user; the first one is to include a folder and the second one to include only a person’s CSV file.
-
A playing control is also added to give functionality to the user to view the environment at that particular timestamp.
-
Another functionality is given to play frame by frame at a specific interval as set by the user in
fpsdrop down box. -
Arrows are also provided to move to the next or previous frame.
-
QTableView is also implemented to view the exact data in realtime as the user move to a new frame.
AGM Integration
-
This component needs to be linked with the AGM so that all the changes will also be reflected in the AGM.
-
For this
agmexecutive_proxyis used and for every new frame a link update is performed usingAGMMisc::publishEdgeUpdatemethod. -
The function
includeInAGMis used to include a person in the AGM.
RCIS Integration
-
To make the person move in the RCIS, we need to make changes in the inner model.
-
This is achieved using the
innermodelmanager_proxy, and we have used a common mesh for all persons that are added. -
The function
includeInRCISis used to include a person in the inner model. -
The function
movePersonsis responsible for all the person movement both in inner model as well as in AGM.